What is Radon?
Radon Facts and Resources
Quick Facts About Radon
|
|
What Is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring, radioactive gas that has no smell, color, or taste. Radon can be found in rocks, air, water, and soil. It is continually produced when uranium and radium decay. Uranium, radium, and radon, like other radioactive elements, are unstable which means they can randomly split apart, releasing energy that is dangerous to human health. All rocks in Utah (and throughout the world) contain these elements and it is difficult to avoid minor levels of radon exposure as a result.
How Does Radon Impact Your Health?
Radon generally enters your lungs by sticking to dust particles in the air. As we breathe, radon particles are deposited on the cells lining the airways and membranes, especially in our lungs. Once inside of our lungs it produces large amounts of harmful radiation. This radiation causes DNA damage inside of your lungs which can lead to lung cancer. Because of this, radon is considered a “Class A Human Carcinogen, “by the US Surgeon General’s Office. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that radon is responsible for more than 25,000 annual deaths, making it the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. According to the World Health Organization, radon causes between 3% to 14% of all lung cancers, depending on the average radon level and the smoking prevalence locally. However, with a little
It is important to understand the health impacts of radon, which including:
- Since radon is a gas, it enters the lungs as you breathe and causes tissue damage that can lead to lung cancer (NIH).
- Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States and the first leading cause among non-smokers (EPA).
- Recent studies have linked radon to an increased risk of stroke (Buchheit et al.)
- Children are at a higher risk than adults of developing lung cancer when exposed to the same amount of radon (US Department of Health and Human Services).
- Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related death in Utah (Utah Department of Health and Human Services).
- Epidemiologic studies of miner cohorts have reported increased frequencies of chronic, nonmalignant lung diseases such as emphysema, Chronic interstitial pneumonia, and Pulmonary fibrosis (CDC).
How do I Know if My Home is Safe?
The EPA defines elevated radon as 4.0 picocuries or above (pCi/L). In the United States, approximately 1 in 15 homes have unsafe radon levels, but here in Utah as many as 1 in 3 homes has elevated radon.
Both new homes and old homes both can have elevated radon because old homes are likely to have more cracks for radon to enter the home, but new homes are insulated and well-sealed to improve the homes efficiency and this can easily trap radon in the home.
Since radon gas is found all around us, it is able to enter our homes through cracks and seams in the foundation, sewer and plumbing lines, and crawl spaces below our homes. Without proper ventilation, radon can build up in the home causing higher concentrations in the basement, crawl space, and the lower floors of the building.
Since the ground changes due to earthquakes, the freezing/thawing cycle, and other industrial practices, the radon levels in your home can change from year to year. As a result, the EPA suggests testing your home every 2-5 years.
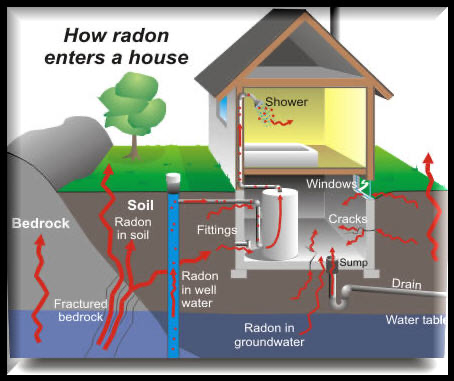
If your home has elevated radon, a radon mitigation system can be installed to remove
the gas from your home. These systems must be installed by a professional, but can
increase the value of your home and provide assurance that your home is healthy.
Testing is Easy, Fast, and Inexpensive
Since radon gas tends to build up most in the winter when the ground is frozen and the windows and doors in the house are closed the most. As a result, testing your home for radon in the Winter (November-February) is most ideal to know your radon risk.
- Reduced price kits are available to Utah residents from the Utah Department of Environmental Quality here.
- Radon tests are also available on Amazon and at most hardware stores for $40/test kit.
- To learn more about how to test your home for radon, go to: https://deq.utah.gov/waste-management-and-radiation-control/test-your-home-for-radon
- You can request a radon test during real estate transactions using a certified radon tester for around $150.
- Please be sure to use a certified professional radon tester for this purpose.
Is Radon a Problem Where You Live? Click here to find out.
